NTT DoCoMo and Mitsubishi Electric hit 27Gbps 5G speeds in car

NTT DoCoMo has announced attaining 5G speeds of 27Gbps during outdoor trials with Mitsubishi Electric in Kamakura, in Japan's Kanagawa Prefecture.
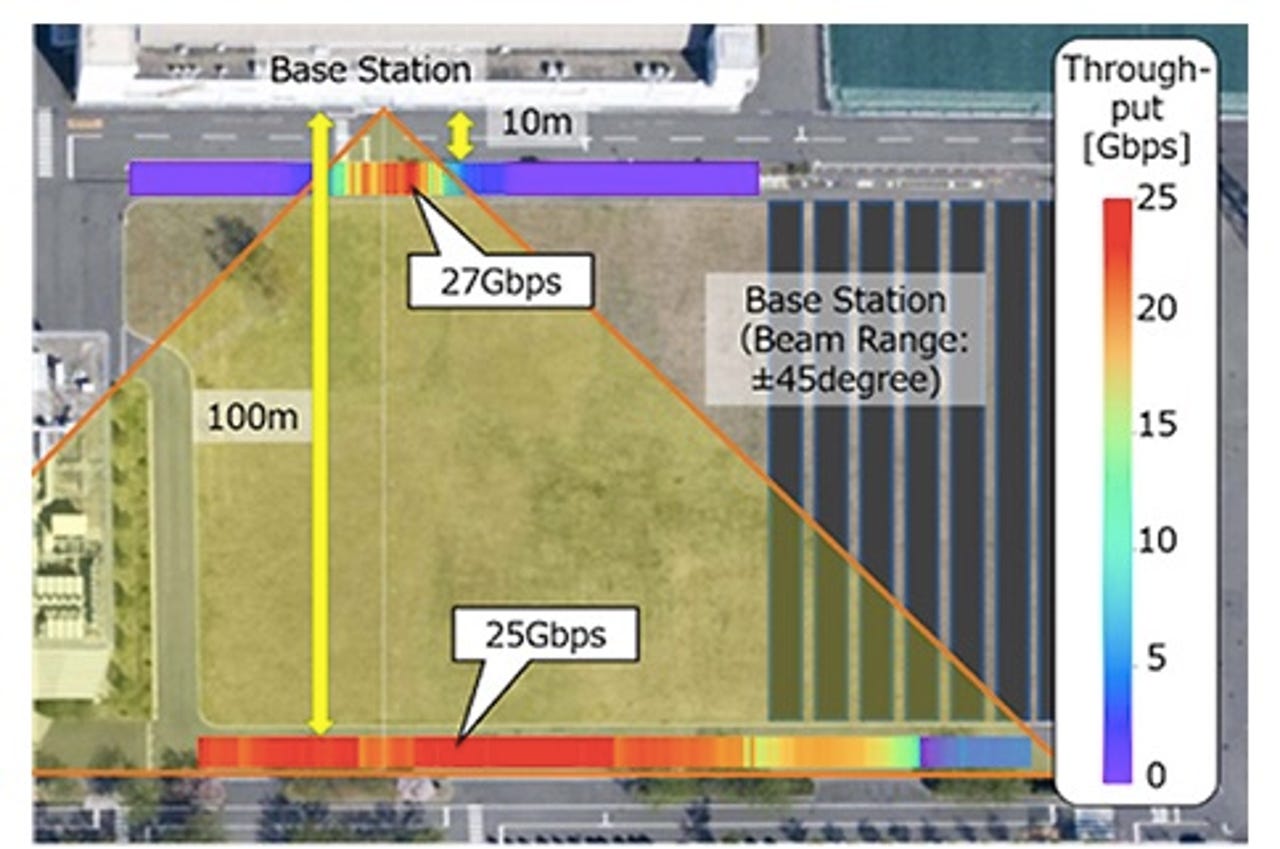
According to the Japanese carrier, this was the world's first 5G transmission to exceed a peak speed of 20Gbps using one terminal, with a communication distance of 10 metres attaining the 27Gbps speed, and a speed of 25Gbps over 100 metres.
NTT DoCoMo used the 28GHz millimetre-wave (mmWave) frequency band, massive-element antenna systems, and 16-beam spatial multiplexing technology with 500MHz bandwidth, which they said could be used to transmit high-speed connectivity to vehicles with multiple passengers such as trains and buses.
"Base-station antennas installed on the wall of a building directed beams to mobile-terminal antennas installed on the rooftop of a vehicle," the companies said, explaining that massive-element antenna systems technology allow for several data streams to be transmitted in parallel.
"The mobile terminal moved along two different streets. The distance of one mobile terminal was 10m from the base station and the distance for the other was 100m."
According to the two companies, they attained the high speeds by developing more advanced beam-forming technology.
"Mitsubishi Electric and DoCoMo developed beam-forming technology in an analog domain and inter-beam interference reduction technology to suitably separate overlapping beams with digital signal processing at the base station. The result is 16-beam spatial multiplexing, which has been unachievable with 4G," they explained.
"The developed beam-forming technology enables beams to track a mobile terminal by switching the preset beam. The inter-beam interference reduction technology estimates the channel at the base station and controls the transmitting signal to adaptively reduce inter-beam interference as channel conditions over time. Together, the two technologies enable 16-beam spatial multiplexing in outdoor mobile environments."
They will next conduct indoor trials before the end of March, with the R&D project being the result of a commission by Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications to look into Massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology for 5G.
NTT DoCoMo has actively been working to push 5G capabilities, completing trials of 5G integrated access backhaul (IAB) technology with Chinese networking giant Huawei in May, which it said increases the wireless coverage of mmWave spectrum.
The field trial used the 39GHz band and was undertaken in Yokohama CBD Minato Mirai 21, testing wireless backhaul between an IAB donor 5G base station and an IAB or 5G relay node, which was able to connect wirelessly with mobile user equipment.
IAB technology reduces interference and allows for simultaneous data transmissions over the same frequency, the telco said.
Huawei and NTT DoCoMo had similarly tested 5G in Yokohama's Minato Mirai 21 District back in 2016, attaining 11.29Gbps throughput speeds and latency of less than 0.5ms during a field trial.
That trial had used the 4.5GHz spectrum band, along with a macro cell with one base station and 23 user equipment devices.
Huawei and NTT DoCoMo signed a memorandum of understanding in December 2014, which also saw the companies conduct an outdoor field trial of Massive MIMO in Chengdu, China.
The Japanese telco giant earlier this year also announced reaching a 5G equipment supply deal with NEC Corporation, with NTT DoCoMo planning to launch its new mobile network in 2020.
Under the deal, NEC will provide control units for 5G base stations as well as using software upgrades to ensure NTT DoCoMo's existing base stations and telco equipment are compatible with 5G.
NEC had in February used Mobile World Congress 2018 to announce that it would be undertaking verification experiments alongside NTT DoCoMo on 5G wireless technologies at the Yokosuka Research Park and NEC's Tamagawa Plant.
Following the standardisation of 5G NR specs in December, NTT DoCoMo, NEC Corporation, and Huawei all announced the beginning of the full-scale development of 5G NR including large-scale trials and commercial deployment, along with Ericsson, Intel, Nokia, Samsung, AT&T, BT, China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, Deutsche Telekom, Fujitsu, KT Corporation, LG Electronics, LG Uplus, MediaTek, Orange, Qualcomm, SK Telecom, Sony Mobile Communications, Sprint, TIM, Telefonica, Telia Company, T-Mobile USA, Verizon, Vodafone, and ZTE.
NTT DoCoMo has also been involved in testing 5G with Ericsson, Nokia, and Intel.
Related Coverage
Quick glossary: 5G technology (Tech Pro Research)
5G will be the key to unlocking the full potential of IoT and a host of other technologies. Businesses can get a jump on their competition if they apply the power of 5G to their products and services first.
Huawei and Spark showcase separated 5G network in New Zealand
Following the Australian government citing a lack of separation of edge and core in 5G, Huawei has demonstrated what it says is full isolation of each network component in New Zealand on a trial network with Spark.
SK Telecom and Samsung to collaborate on 5G for enterprise
SK Telecom and Samsung will collaborate in 5G research and development, including in augmented reality, as rollout in the enterprise gears up for next month.
Telstra connects device to 5G with Ericsson and Qualcomm
Telstra has used a Qualcomm 5G chipset and device with Ericsson 5G software and its own 3.5GHz spectrum to achieve a live 5G connection.
Huawei and Three UK trial 5G home broadband
Huawei is still actively playing in the UK's 5G market, this week announcing trials of home broadband services with Three UK using commercial 5G routers that attained download speeds of up to 2Gbps.
T-Mobile announces 5G connection with Nokia
Nokia and T-Mobile have successfully transmitted 5G data using low-band spectrum, which they say will provide 5G coverage to the entire nation by 2020.
How 5G technology will change data centers (TechRepublic)
The content and telco functionality in data centers will slowly change over the next two years with the addition of 5G.
5G mobile networks: A cheat sheet (TechRepublic)
As LTE networks become increasingly saturated, mobile network operators are planning for the 5G future. Here is what business professionals and mobile users need to know about 5G networks.