OpenStack 101: Getting started with Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform
Cloud computing is enjoying a growing presence in businesses today, and according to forecasts from experts such as Gartner, uptake is only set to rise in the future.
As organizations that haven't already latched onto the trend look to do so, investing in the right infrastructure, technology and tools is essential. OpenStack, as a community project, is not yet ready for the enterprise 'as-is'. However, like other popular open source community projects including Linux, there are companies, including Red Hat, that are making the community project into an enterprise Infrastructure-as-a-Service offering, enabling organizations to attain greater agility and scalability with the cloud, with the support lifecycle, vast partner ecosystem, and certified solutions portfolio that enterprise customers require.
As OpenStack moves into the enterprise, there are a number of installation best practices organizations should consider. For any organization that is interested in getting started with OpenStack, we've pulled together the following guide to help you get started.
A guide to the OpenStack architecture
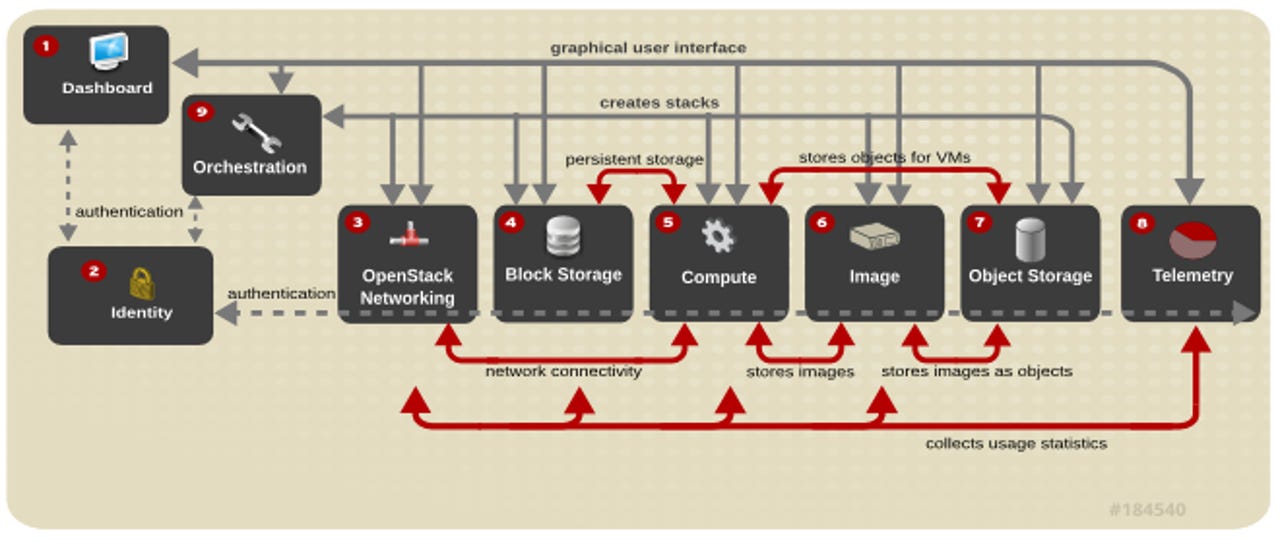
The entire OpenStack system - known as its architecture - can appear complex at first glance. There is an extensive list of services and components that work together, and which can be tailored to meet the unique needs of different enterprises.
As such, it pays to get to know some of the most critical features before starting installation. One of the parts users will be interacting most with is OpenStack Dashboard (Horizon), which acts as the dashboard for the entire cloud infrastructure. Through this web-based interface, users can complete a range of tasks, including launching instances and managing a range of access controls.
OpenStack Compute (Nova) is another crucial component of the architecture, enabling the easy management of multiple virtual machines across the network. A range of other storage, shared and higher-level services work in the background to keep the system running.
Four OpenStack terms you must know
In addition to the numerous parts of the architecture, working with OpenStack involves using highly specialized terminology - some of which can seem like an entirely different language. However, anyone can soon pick it up when they start using it - here are just four to get you started.
1. Tenant: These refer to groups within the architecture - whether they be of users, instances, networks or other.
3. Compute node: Another term for a hypervisor, or any machine running Nova Compute.
4. Instance: This is simply another word for a virtual machine deployed within the cloud.
5. Flavor: The flavor refers to all hardware associated with an instance, including RAMs and disks.
Do you have the right system requirements?
As with all types of software and enterprise applications, you should ensure your organization's existing systems have the specifications to host the OpenStack platform.
As outlined in the Red Hat OpenStack Administration (CL210) course, you must have at least two machines with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 64-bit - version 6.4 or later - in order to run OpenStack. You can assign one of these machines as the dedicated cloud controller, while the other can be deployed as a Nova Compute node. It is recommended that you have at least two Nova Compute nodes in operation.
Where can I get further help?
After installing and deploying OpenStack, it can be natural to want a bit of guidance at times. Thankfully, with the proliferation of the platform, there are numerous free guides across the internet to help users out. These come in a variety of formats, from text guides to video tutorials, and many are quite comprehensive.
A number of dedicated articles, such as these two, collate some of the guides from around the web that we've found useful into one convenient location for your handy reference.
Investing in Red Hat's training courses can also help not only you, but your entire team, get the most out of OpenStack and use it to its full potential. With a range of different delivery models, from classroom (physical and virtual) to on-premise learning, there is an option for just about every enterprise.
To learn more about the best practices involved in getting started with Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform, download your copy of the Red Hat whitepaper today.