New Qualcomm auto chipset advances vehicle-to-everything communications

Qualcomm on Friday is introducing a new Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X) chipset and reference design that should bring automakers one step closer to deploying the communications systems needed for fully autonomous vehicles.
The Qualcomm 9150 C-V2X chipset, expected to be available for commercial sampling in the second half of 2018, is based on specs from the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), a collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations.
Meanwhile, Qualcomm's C-V2X reference design will feature the 9150 C-V2X chipset, an application processor running the Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) V2X stack, as well as a Hardware Security Module (HSM).
Qualcomm already has mulitple automotive partners endorsing the new chipset, including Ford, Audi, the PSA Group and SAIC.
"We welcome Qualcomm Technologies' cellular-V2X product announcement, as the automotive industry and ecosystem work towards C-V2X implementation, and pave the path to 5G broadband and future operating services," Don Butler, executive director of Connected Vehicle and Services at Ford, said in a statement.
As C-V2X standards evolve, "there is an increasing appetite to say, 'Let's test it out,'" Durga Malladi, SVP of engineering at Qualcomm, said to ZDNet. "And for that, we need a chipset."
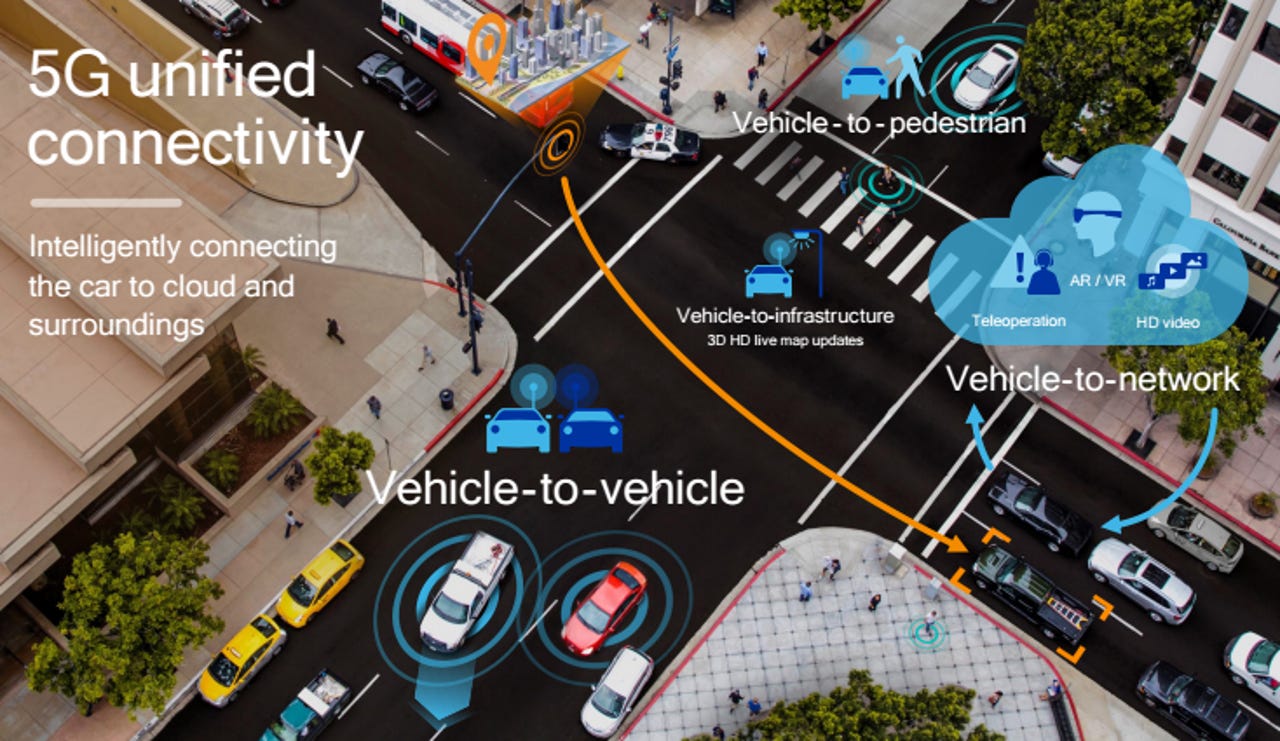
C-V2X technology encompasses two transmission modes: direct communications and network-based communications. It's key for both safety features and for implementing autonomous driving capabilities.
For instance, its direct communications capabilities improve a vehicle's situational awareness by detecting and exchanging information using low latency transmissions. Relying on the globally harmonized 5.9 GHz ITS band, the 9150 C-V2X chipset can relay information on vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) and vehicle-to-pedestrian (V2P) scenarios without the need for a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM), cellular subscription or network assistance.
On top of that, C-V2X network-based communications (designed for 4G and emerging 5G wireless networks) supports telematics, connected infotainment and a growing number of advanced informational safety use cases.
In the 9150 C-V2X chipset, all of this translates into enhanced V2X capabilities like extended communication range, improved reliability and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) performance. With integrated global navigation satellite system (GNSS) support, it offers precise positioning for vehicles -- a feature that's key for safety and basic functionality of driverless cars.
With extended communication capabilities and precise positioning, Malladi explained, a car will eventually be able to communicate not just with the cars next to it, but with all cars within a certain range.
"Now you can start thinking about path planning," he said, "This is a glimpse of what's possible" with fully autonomous driving.
The C-V2X chipset is Qualcomm's latest demonstration of its interest in the automotive market. Last fall, Qualcomm reached a deal to acquire NXP Semiconductor for $47 billion to help it move into IOT and automotive. The deal, however, is still under review by regulators.
Earlier this year, Qualcomm published a report concluding that by 2035, 5G will enable more than $2.4 trillion in total economic output across the automotive sector, its supply chain, and its customers.
Related coverage:
Magna launches MAX4 system, aims to scale autonomous driving broadly
Bosch, Nvidia, Grab join Baidu's autonomous driving alliance
European Commission opens investigation into Qualcomm, NXP deal