Vulnerabilities discovered in Windows security protocols

Two vulnerabilities have been uncovered in Microsoft Windows security protocols which could lead to password cracking and domain compromise, researchers have warned.
Featured
This week, the Preempt security team said the bugs were discovered in the Microsoft Windows NT LAN Manager (NTLM) security protocols, a security software suite which replaced the older Windows LAN Manager (LANMAN) platform.
According to Preempt, the vulnerabilities relate to different protocols handling NTLM improperly.
"These issues are particularly significant as they can potentially allow an attacker to create new domain administrator accounts even when best-practice controls such as LDAP server signing and RDP restricted admin mode are enabled," the company says.
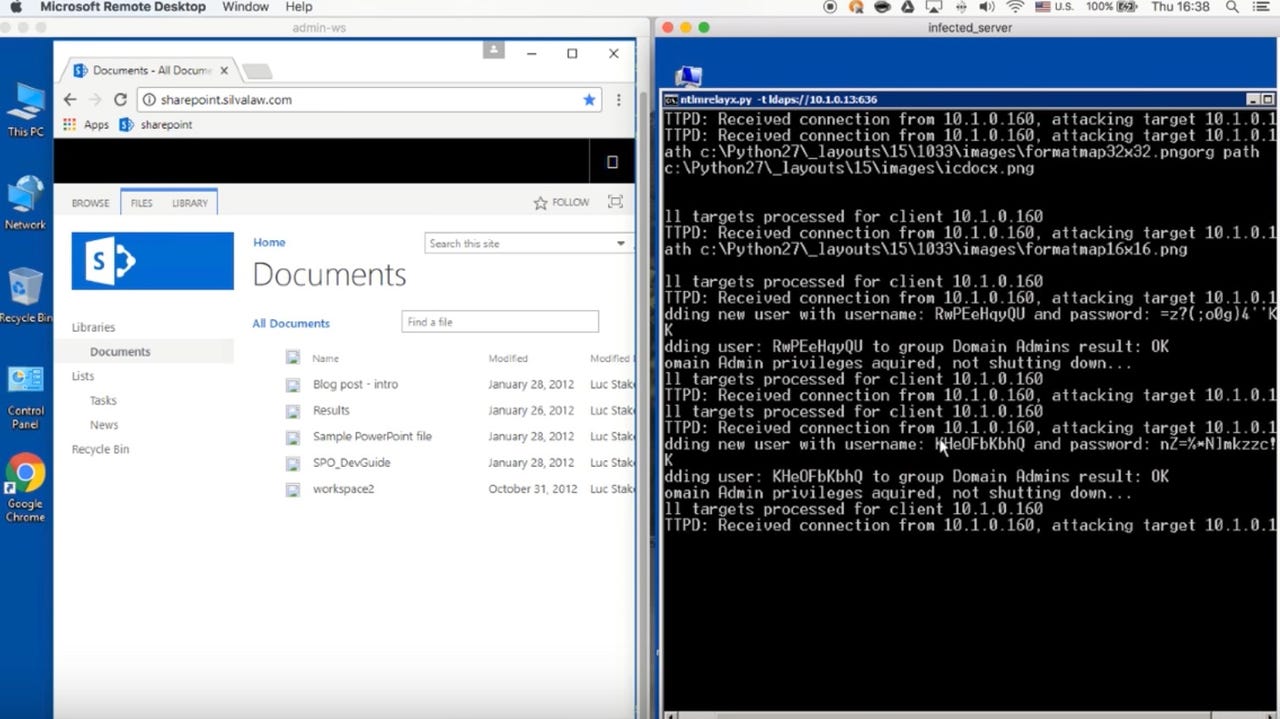
The first vulnerability, CVE-2017-8563, relates to an unprotected Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) from an NTLM relay.
LDAP is meant to protect against Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks and credential forwarding, but the security flaw means that this does not always protect against credential forwarding.
As such, when Windows protocols use the Windows Authentication API (SSPI) -- which allows the downgrade of an authentication session to NTLM -- every session can be compromised if connected to an infected machine.
If a compromised system has a domain admin, then attackers can create an administrator account which gives them control over an attacked network.
The second issue, which is not CVE assigned, relates to RDP Restricted-Admin Mode. Preempt says that users are able to connect to a remote machine without volunteering their password to the remote machine that might be compromised.
"DP Restricted-Admin Mode allows users to connect to a remote machine without volunteering their password to the remote machine that might be compromised," the team says. "As a result, every attack performed with NTLM, such as credential relaying and password cracking, could be carried out against RDP Restricted-Admin.
"Each time an admin connects with protocols such as RDP Restricted-Admin, HTTP or File Share (SMB), an attacker could potentially create a rogue domain admin, demonstrating the significance of these findings in the NTLM security protocol," the team added.
Preempt reported the bugs to Microsoft on April 2. Within four days Microsoft acknowledged the initial report, and after a further three days, both issues were acknowledged.
For CVE-2017-8563, a fix was released as part of July's Patch Tuesday, and for the second issue, Microsoft said it is a "known issue" which requires network configuration to prevent malicious NTLM relays.
According to Preempt, using NTLM at all is very risky, but if companies must use the protocol on their network, they should make LDAP authentication over SSL/TLS more secure, install the patch for CVE-2017-8563 on all domain controllers if automatic updates are not enabled, and enable "Require LDAP Signing" in GPO settings.
See also: Microsoft releases emergency patch for 'crazy bad' Windows zero-day bug
As part of Microsoft's monthly Patch Tuesday release, the Redmond giant patched 54 vulnerabilities in Windows, Edge, Internet Explorer, Office, and Exchange. In total, 19 bugs were deemed critical.