Google awards $2.9 million for bug bounties in 2017

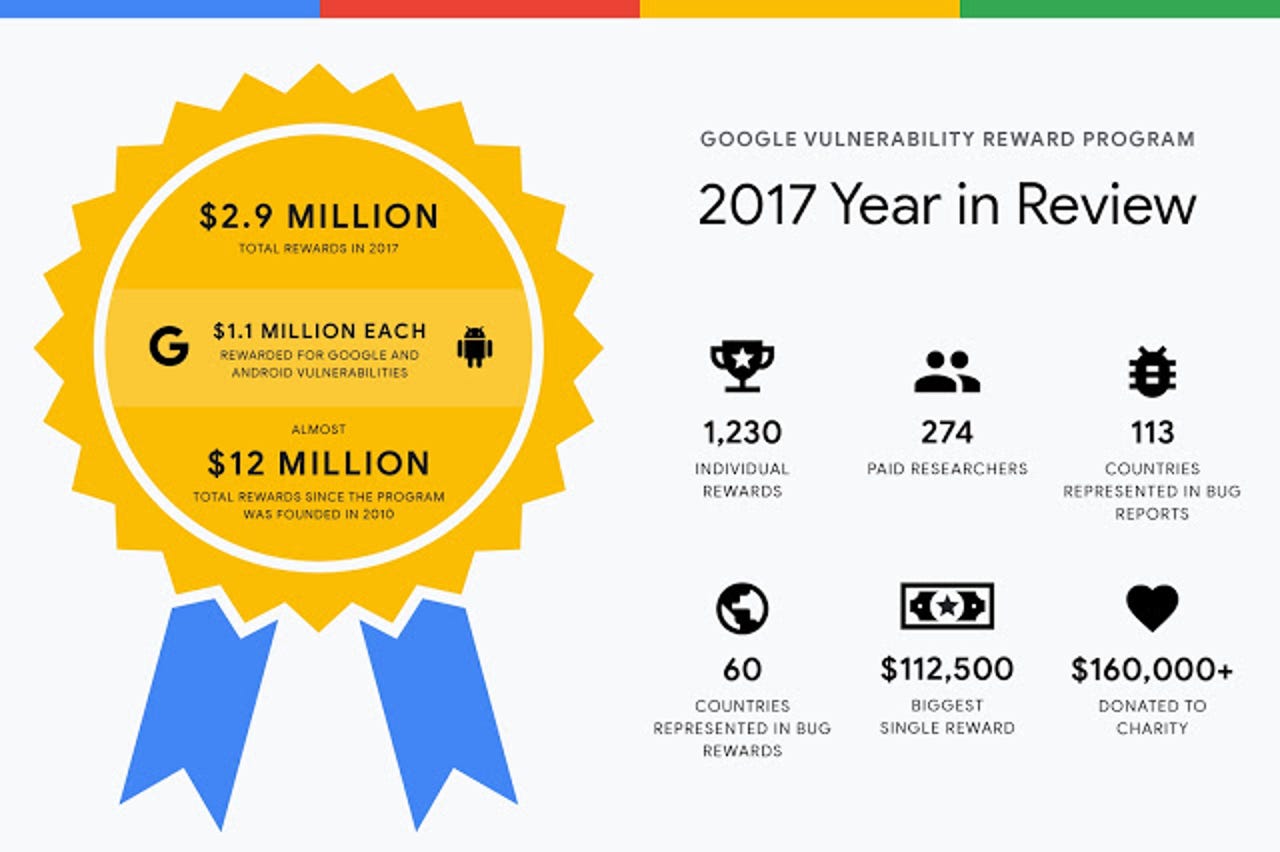
Google on Wednesday revealed it paid out $2.9 million in 2017 as part of its bug bounty program that rewards researchers for their vulnerability reports. Since launching the program in November 2010, Google said it has paid out almost $12 million to security researchers.
In 2017, Google paid 274 researches total, and issued its largest award ever of $112,500 to a security researcher for reporting an exploit chain that could be used to compromise Pixel mobile devices.
Google and Android vulnerabilities made up $1.1 million each for the year, with Chrome filling in the rest, the company revealed in a blog post.
In 2016, Google paid $3 million to researchers for vulnerability reports.
Google highlighted two other big vulnerabilities from 2017:
- Researcher "gzobqq" received the $100,000 pwnium award for a chain of bugs across five components that achieved remote code execution in Chrome OS guest mode.
- Alex Birsan discovered that anyone could have gained access to internal Google Issue Tracker data and was awarded $15,600 for his efforts.
Further, Google said it awarded $125,000 to more than 50 security researchers worldwide through its Vulnerability Research Grants Program, and awarded $50,000 to improve the security of open-source software as part of its Patch Rewards Program.
Google will expand the range of rewards for research for remote code executions in Android apps on Google Play from $1,000 to $5,000, it also revealed.
Google also introduced a new category that includes vulnerabilities that could end in theft of users' private data, information being transferred unencrypted, or bugs that result in access to protected app components. Google will award $1,000 for these bugs.