Microsoft's Windows Server 2012 now powering all Bing searches worldwide

When Microsoft delivered the near-final Release Candidate (RC) of Windows Server 2012 on May 31, company officials told me there were no new features introduced to the product since the beta hit in late February.
So does that mean Windows Server 2012 is, for all intents and purposes, "done" -- as opposed to Windows 8 client, which is still being modified considerably even though the Softies are calling it "feature-complete"? In a word, yes.
And if you need more proof of Windows Server 2012's sea-worthiness, Microsoft announced on June 7 that the company is is serving up all worldwide results from Bing.com using Windows Server 2012 servers running the Release Candidate.
In a post to the Windows Server blog on June 7, Mukul Sabharwal, a software development engineer on the Bing team, said that "Bing is adopting and deploying Windows Server 2012 as fast as they can" because the coming Windows Server release is basically a cloud-optimized on-premises operating system.
Sabharwal said the Bing team is taking advantage of four of Windows Server 2012's features in particular:
- Built-in Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5, included with Windows Server 2012, including the background garbage collection and associated improved latencies
- Improved performance at startup, enabled by the multicore JIT (just in time) functionality of .NET 4.5
- Ability to collect call stacks for 64-bit .NET JITted applications
- Evaluation of Hyper-V 3 (the version of Hyper-V in Window Server 2012)
"What began as exploratory evaluations of the impact of a migration quickly led to a full-scale deployment," Sabharwal said.
It's worth noting that just because there were technically "no new features" introduced between the Beta and Release Candidate of Windows Server 2012 doesn't mean there were no improvements made between the two milestones. In fact, Microsoft made a number of performance tweaks to the operating system since the beta was downloaded more than 300,000 times.
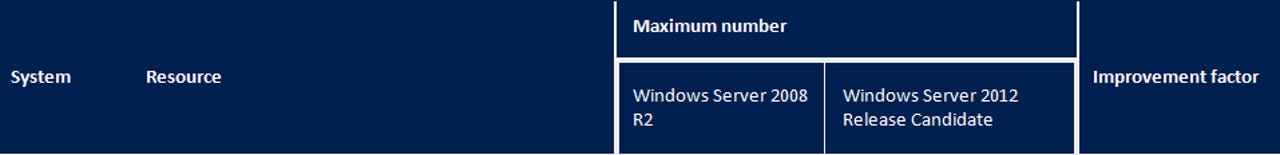
Microsoft officials shared this chart, showing what's changed, performance- and scale-wise since the company delivered Windows Server 2008 R2 and the Windows Server 2012 RC;
(click on table above to enlarge)
In terms of what's changed between the beta and the RC, there's not much information company officials are sharing.
In related Server news today, Microsoft has released version 3.3 of its Linux integration Services.
As Microsoft Most Valuable Professional Aidan Finn noted, the latest iteration supports the versions of Hyper-V hypervisors that are part of Windows 8 Release Preview and Windows Server 2012. (Linux Integration Services already supported Hyper-V in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2.)
The supported guest operating systems now include:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.0-6.2 x86 and x64 (Up to 4 vCPU)
- CentOS 6.0-6.2 x86 and x64 (Up to 4 vCPU)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.0-6.2 x86 and x64 (Up to 32 vCPU when used on a Windows 8 Release Preview or Windows Server 2012 host)
- CentOS 6.0-6.2 x86 and x64 (Up to 32 vCPU when used on a Windows 8 Release Preview or Windows Server 2012 host)
"RHEL 6.2 and CentOS 6.2 were added to the list in v3.3," according to Finn.
The Microsoft code is based on the latest version of the code upstream in the Linux kernel, backported to the kernel that is used in RHEL and CentOS 6. With this update, all the drivers have exited the staging tree of the Linux kernel, and are now part of the kernel itself, I've heard.