A graph is a graph is graph? RDF vs LPG

Graph = Vertices + Edges
Graph = Vertices + Edges. But it's a bit more complicated than that. Image: Jesus Barrasa, Director Telecoms Practice, Neo4j
RDF works in triples
RDF works in triples. Subject, Predicate, Object. For instance, Tom is a human. Image: Jesus Barrasa, Director Telecoms Practice, Neo4j
RDF Vertices + Edges
In RDF, vertices can be resources (having Uniform Resource Identifiers as their IDs) or literal primary values. Edges are relationships also having URIs as their IDs. Image: Jesus Barrasa, Director Telecoms Practice, Neo4j
LPG works in connected things
LPG is about describing vertices with properties, and connecting them with edges. Tom is a human with age = 12 and eye color = blue, and he likes ice cream. Image: Jesus Barrasa, Director Telecoms Practice, Neo4j
LPG Vertices + Edges
In LPG, vertices are nodes with an ID and a set of key-value pair properties, and edges are relationships also having an ID and a set of key-value pair properties. Image: Jesus Barrasa, Director Telecoms Practice, Neo4j
RDF graphs visualized
RDF graphs can be quite extensive as a result of the way they model the world. Image: Jesus Barrasa, Director Telecoms Practice, Neo4j
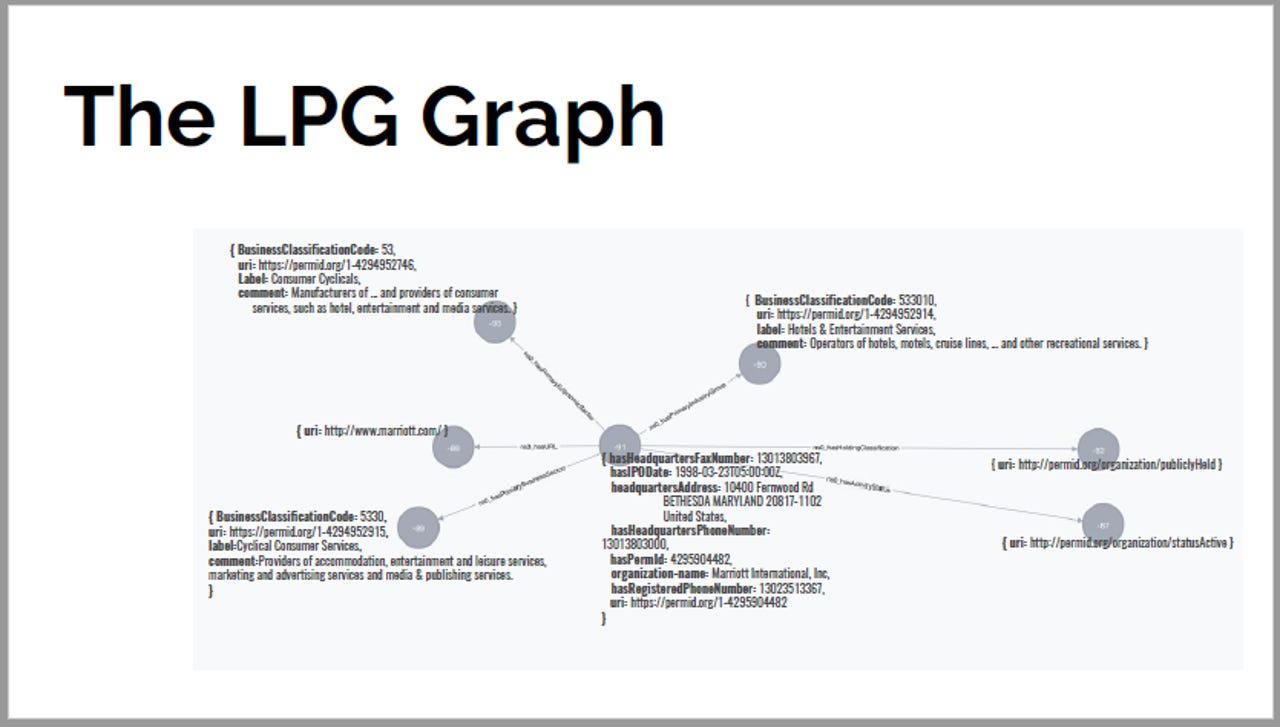
LPG graphs visualised
LPG graphs are more condensed, as a result of the way they model the world. Image: Jesus Barrasa, Director Telecoms Practice, Neo4j